|
libfoedus-core
FOEDUS Core Library
|
|
libfoedus-core
FOEDUS Core Library
|
Procedure manager, which maintains the list of system/user procedures. More...
Procedure manager, which maintains the list of system/user procedures.
Definition at line 35 of file proc_manager.hpp.
#include <proc_manager.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| ProcManager (Engine *engine) | |
| ~ProcManager () | |
| ProcManager ()=delete | |
| ProcManager (const ProcManager &)=delete | |
| ProcManager & | operator= (const ProcManager &)=delete |
| ErrorStack | initialize () override |
| Acquires resources in this object, usually called right after constructor. More... | |
| bool | is_initialized () const override |
| Returns whether the object has been already initialized or not. More... | |
| ErrorStack | uninitialize () override |
| An idempotent method to release all resources of this object, if any. More... | |
| ErrorStack | get_proc (const ProcName &name, Proc *out) |
| Returns the function pointer of the specified procedure. More... | |
| ErrorStack | pre_register (const ProcAndName &proc_and_name) |
| Pre-register a function pointer as a user procedure so that all SOCs will have it when they are forked. More... | |
| ErrorStack | pre_register (const ProcName &name, Proc proc) |
| Just a synonym. More... | |
| const std::vector< ProcAndName > & | get_pre_registered_procedures () const |
| Returns procedures given to pre_register() More... | |
| ErrorStack | local_register (const ProcAndName &proc_and_name) |
| Register a function pointer as a user procedure in the current SOC. More... | |
| ErrorStack | emulated_register (const ProcAndName &proc_and_name) |
| Register a function pointer as a user procedure in all SOCs, assuming that child SOCs are of kChildEmulated type. More... | |
| std::string | describe_registered_procs () const |
| For debug uses only. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from foedus::Initializable Public Member Functions inherited from foedus::Initializable | |
| virtual | ~Initializable () |
|
explicit |
Definition at line 28 of file proc_manager.cpp.
| foedus::proc::ProcManager::~ProcManager | ( | ) |
Definition at line 31 of file proc_manager.cpp.
|
delete |
|
delete |
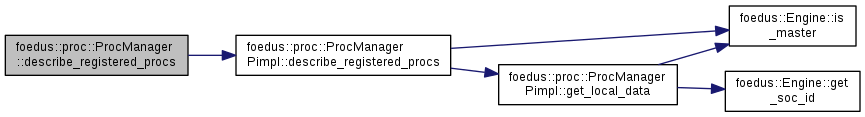
| std::string foedus::proc::ProcManager::describe_registered_procs | ( | ) | const |
For debug uses only.
Returns a summary of procedures registered in this engine
Definition at line 57 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::proc::ProcManagerPimpl::describe_registered_procs().
Referenced by foedus::soc::SocManagerPimpl::child_main_common().
| ErrorStack foedus::proc::ProcManager::emulated_register | ( | const ProcAndName & | proc_and_name | ) |
Register a function pointer as a user procedure in all SOCs, assuming that child SOCs are of kChildEmulated type.
This can be used any time after the initialization and also takes effect in all SOCs. However, this can be used only with kChildEmulated SOCs. Most testcases and small programs that do not need high scalability can use this.
Definition at line 50 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::proc::ProcManagerPimpl::emulated_register().

| const std::vector< ProcAndName > & foedus::proc::ProcManager::get_pre_registered_procedures | ( | ) | const |
Returns procedures given to pre_register()
Definition at line 54 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::proc::ProcManagerPimpl::pre_registered_procs_.
Referenced by foedus::soc::SocManagerPimpl::emulated_child_main(), and foedus::soc::SocManagerPimpl::forked_child_main().

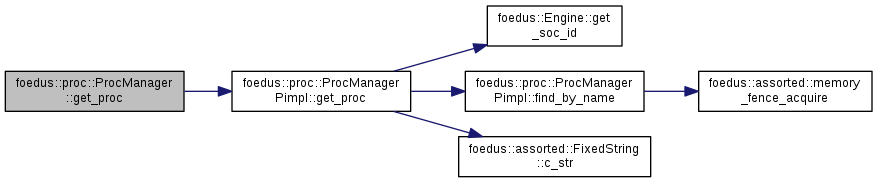
| ErrorStack foedus::proc::ProcManager::get_proc | ( | const ProcName & | name, |
| Proc * | out | ||
| ) |
Returns the function pointer of the specified procedure.
| [in] | name | Name of the procedure that has been registered via one of the following methods |
| [out] | out | Function pointer of the procedure. |
Definition at line 40 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::proc::ProcManagerPimpl::get_proc().
Referenced by foedus::thread::ThreadPimpl::handle_tasks().

|
overridevirtual |
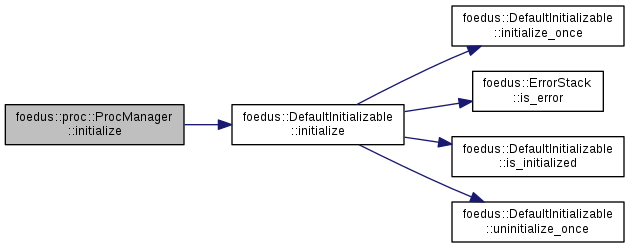
Acquires resources in this object, usually called right after constructor.
If and only if the return value was not an error, is_initialized() will return TRUE. This method is usually not idempotent, but some implementation can choose to be. In that case, the implementation class should clarify that it's idempotent. This method is responsible for releasing all acquired resources when initialization fails. This method itself is NOT thread-safe. Do not call this in a racy situation.
Implements foedus::Initializable.
Definition at line 36 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::DefaultInitializable::initialize().
|
overridevirtual |
Returns whether the object has been already initialized or not.
Implements foedus::Initializable.
Definition at line 37 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::DefaultInitializable::is_initialized().
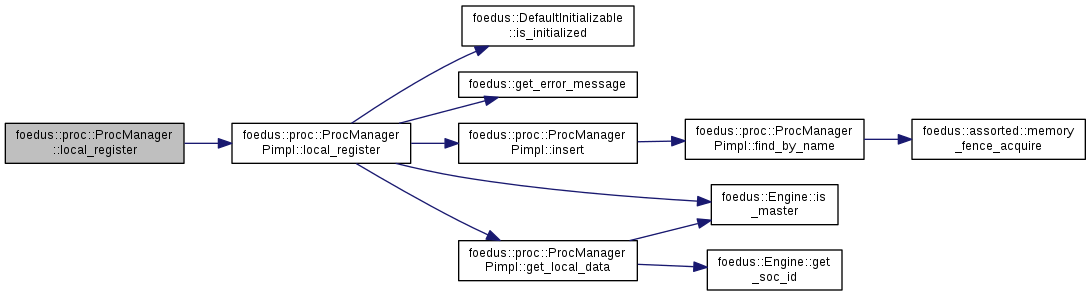
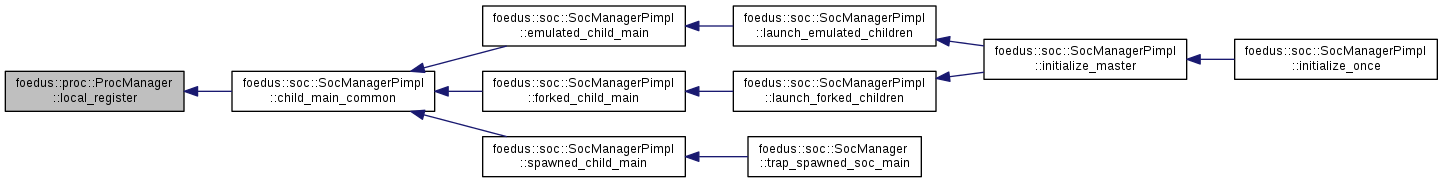
| ErrorStack foedus::proc::ProcManager::local_register | ( | const ProcAndName & | proc_and_name | ) |
Register a function pointer as a user procedure in the current SOC.
This can be used any time after the initialization, but it takes effect only in the current SOC. Function pointers cannot be shared with other processes.
Definition at line 47 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::proc::ProcManagerPimpl::local_register().
Referenced by foedus::soc::SocManagerPimpl::child_main_common().
|
delete |
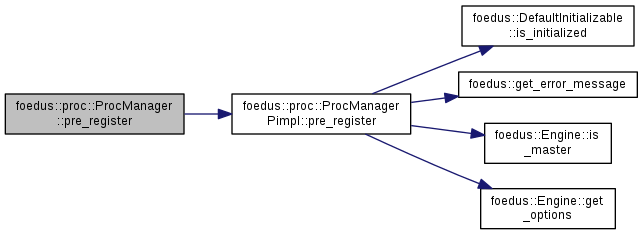
| ErrorStack foedus::proc::ProcManager::pre_register | ( | const ProcAndName & | proc_and_name | ) |
Pre-register a function pointer as a user procedure so that all SOCs will have it when they are forked.
This can be used only for kChildEmulated or kChildForked because function pointers can be shared only when the function pointers are finalized before the fork, or in the same process. So, once Engine is initialized, this method always fails.
Definition at line 44 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::proc::ProcManagerPimpl::pre_register().
Referenced by pre_register().
|
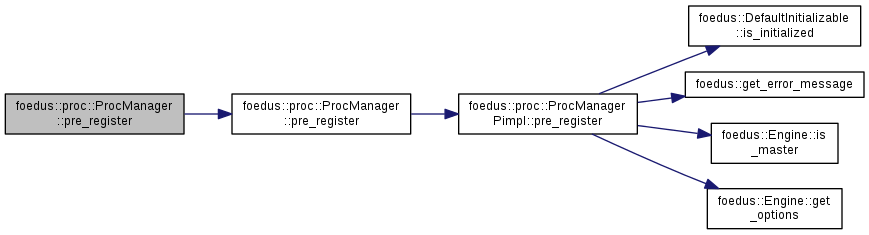
inline |
Just a synonym.
Definition at line 70 of file proc_manager.hpp.
References pre_register().
|
overridevirtual |
An idempotent method to release all resources of this object, if any.
After this method, is_initialized() will return FALSE. Whether this method encounters an error or not, the implementation should make the best effort to release as many resources as possible. In other words, Do not leak all resources because of one issue. This method itself is NOT thread-safe. Do not call this in a racy situation.
Implements foedus::Initializable.
Definition at line 38 of file proc_manager.cpp.
References foedus::DefaultInitializable::uninitialize().
